For my application I use a RTC. For now without SD and based on SDK 11.0. Later I will implement it in an application with BLE. My device is a Raytac module with a nRF52832 on it. The module is connected with the RTC DS1307.
I think that I had success with write to the RTC. Because I get an ACK(NRF_DRV_TWI_EVT_DONE) back after the sequences. But I wont get anything when I try to read the registers of the RTC.
I assume that when I get a NRF_DRV_TWI_EVT_DONE this means, that the TX was successful and this is an ACK?
Does anyone have experience with the DS1307? What should I do, to get the data from the RTC?
And how many bytes do I have to expect to recieve?
Here my code:
#define SCL_PIN 15
#define SDA_PIN 14
#define SLAVE_ADRESSE_W 0x68
#define SLAVE_ADRESSE_R 0x69
#define SEKUNDEN_ADRESSE 0x00
#define MINUTEN_ADRESSE 0x01
#define STUNDEN_ADRESSE 0x02
#define TAG_ADRESSE 0x03
#define DATUM_ADRESSE 0x04
#define MONAT_ADRESSE 0x05
#define JAHR_ADRESSE 0x06
#define WERT_ADRESSE 0x05
uint8_t data[3]; //Array für Daten(3Bytes)
void DS1307_set_mode(void)
{
ret_code_t err_code;
uint8_t reg[2] = {SEKUNDEN_ADRESSE, WERT_ADRESSE};
err_code = nrf_drv_twi_tx(&m_twi_driver, SLAVE_ADRESSE_W, reg, sizeof(reg), false);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
while(m_set_mode_done == false);
}
void read_data()
{
uint8_t higher_byte; //Variabel für höcherwertiges Byte aufsetzen
uint8_t lower_byte; //Variabel für niederwertiges Byte aufsetzen
higher_byte = data[0];
lower_byte = data[1];
}
void twi_handler(nrf_drv_twi_evt_t const * p_event, void * p_context)
{
ret_code_t err_code;
switch(p_event->type)
{
case NRF_DRV_TWI_EVT_DONE:
if ((p_event->type == NRF_DRV_TWI_EVT_DONE) && (p_event->xfer_desc.type == NRF_DRV_TWI_XFER_TX))
{
nrf_drv_twi_rx(&m_twi_driver, SLAVE_ADRESSE_R, (uint8_t*)data, sizeof(data));
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
read_data();
}
if ((p_event->type == NRF_DRV_TWI_EVT_DONE) && (p_event->xfer_desc.type == NRF_DRV_TWI_XFER_RX))
{
nrf_drv_twi_rx(&m_twi_driver, SLAVE_ADRESSE_R, (uint8_t*)data, sizeof(data));
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
read_data();
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void twi_init (void)
{
ret_code_t err_code;
const nrf_drv_twi_config_t twi_mma_7660_config = {
.scl = SCL_PIN,
.sda = SDA_PIN,
.frequency = NRF_TWI_FREQ_100K,
.interrupt_priority = APP_IRQ_PRIORITY_HIGH
};
err_code = nrf_drv_twi_init(&m_twi_driver, &twi_mma_7660_config, twi_handler, NULL);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
nrf_drv_twi_enable(&m_twi_driver);
}
int main(void)
{
twi_init();
DS1307_set_mode();
while(true)
{
}
}
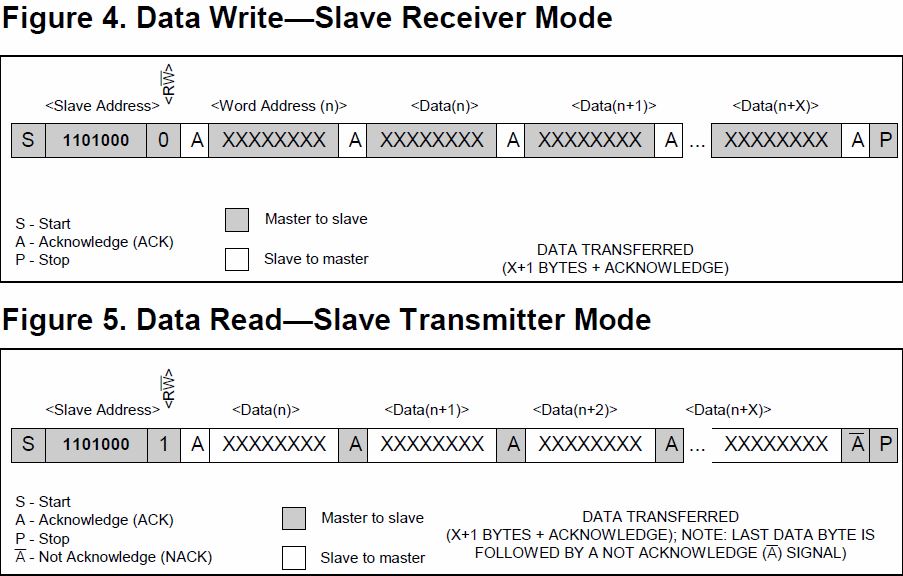
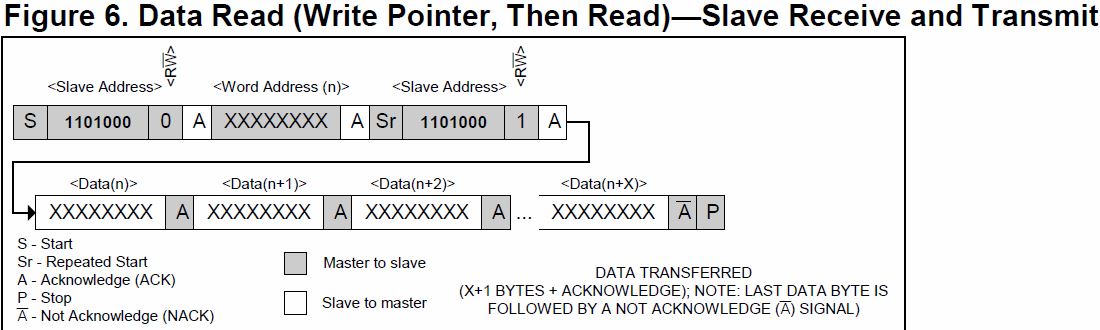
From the Datasheet:
Depending upon the state of the R/W bit, two types of data transfer are possible:
-
Data transfer from a master transmitter to a slave receiver. The first byte transmitted by the master is the slave address. Next follows a number of data bytes. The slave returns an acknowledge bit after each received byte. Data is transferred with the most significant bit (MSB) first.
-
Data transfer from a slave transmitter to a master receiver. The first byte (the slave address) is transmitted by the master. The slave then returns an acknowledge bit. This is followed by the slave transmitting a number of data bytes. The master returns an acknowledge bit after all received bytes other than the last byte. At the end of the last received byte, a “not acknowledge” is returned.
The master device generates all the serial clock pulses and the START and STOP conditions. A transfer is ended with a STOP condition or with a repeated START condition. Since a repeated START condition is also the beginning of the next serial transfer, the bus will not be released. Data is transferred with the most significant bit (MSB) first.