Hello,
I have a custom hardware, with an external 128MB QSPI flash memory connected to a nRF5340. My current task at hand, is to store firmware update images for MCUBoot there. The firmware is stored by the application using a custom driver for the external flash memory.
I've used nrfjprog already, to read measurement data from that external flash memory and that worked quite well. That's why it toke me quite some time to realize, that nrfjprog is doing something stupid here.
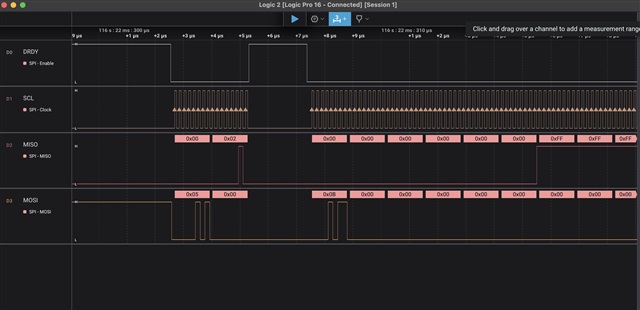
The external flash memory has a page size of 4kB and when reading the flash memory content, every first byte of every empty page reads 0x0f instead of 0xff. I changed the operations to be used to a single data line (read_mode = "FASTREAD"; write_mode = "PP") and slowed down the QSPI clock frequency to M2. Attaching a logic analyser, shows, that the flash memory response with 0xff (not 0x0f) to page read request.
Before opening this request, I updated the Segger JLink software to the newest version and then, the next try to read the flash content, showed the correct results! I did an other test and used `
west build --pristine -b"nrf5340dk/nrf5340/cpuapp" --build-dir ./build --sysbuild .` && `west flash --recover ` to install new firmware on the nRF53. A following read, using nrfjprog showed again, wrong results (0x0f at the begin of every page), while the logic analyser still shows the correct picture.
I power reset, both custom hardware and debugger (J-Trace Pro) but that didn't fixed the issue. Combined with my observation from this ticket (https://devzone.nordicsemi.com/f/nordic-q-a/115570/using-mcuboot-with-nrf5340), that sometimes build errors are not reproducible, my suspicion is, that the `west build` or `west flash` command is changing some configuration data outside of the build folder.
I've used ´nrfjprog` a few month ago and could not find any issues. What changed to the project, was an update to nRF Connect SDK v2.7.99-cs2.
nrfjprog version: 10.24.2 external
JLinkARM.dll version: 8.10d
Here, a screen shot of the QSPI trace:
% nrfjprog --readqspi recording.bin --qspiini ./config.toml [ #################### ] 0.000s | Reading external memory, 0x200000 bytes @ 0x00000000 - Done Storing data in 'recording.bin'. % hexdump -C recording.bin | head 00000000 0f ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff |................| 00000010 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff |................|
Attached is the entire trace and the used configuration file.
Best regards
Torsten

