Hi,
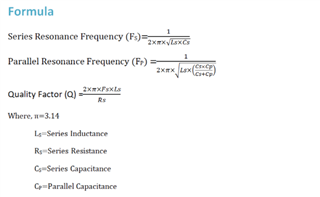
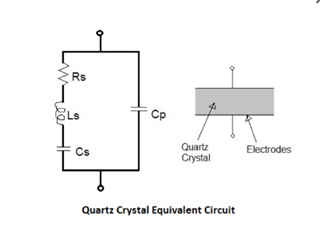
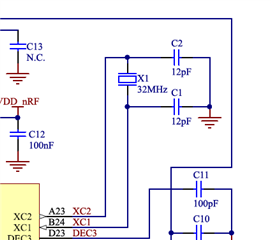
1. Configuration: Recommended crystal oscillator circuit: C1 = 12pF C2 = 12pF
2. Configuration: Crystal oscillator circuit used by the customer: C1 = 10pF C2 = 10pF
3. What formula can be used to calculate the theoretical frequency deviation: for example, the theoretical frequency deviation between configuration 1 and configuration 2
Thank you for all your assistance.
Kind regards,
Peter.Min