Hi everyone,
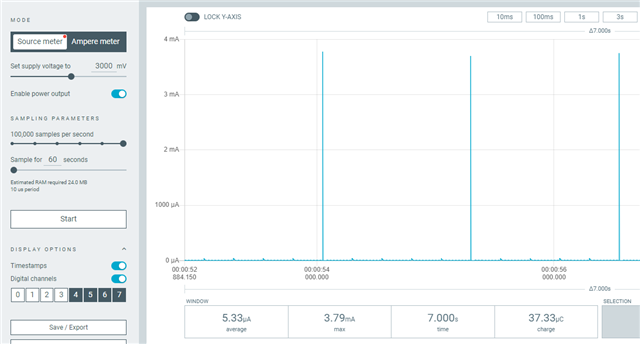
I experiment with the saadc low power example. I have followed all the settings but I cannot achieve as low power as the example. As you can see from the PPK II capture, during sampling the current is around 3.6mA and this raises the average current to 9.82uA (almost double than the example). Any suggestion why the current consumption during sampling is so high?
This is my main.c. The only changes I did was to enable the Burst mode and set the oversample to 4x (both settings suggested by the example)
Also, I have disabled the RTT and UART backends.
#define RTC_FREQUENCY 32 //Determines the RTC frequency and prescaler
#define RTC_CC_VALUE 8 //Determines the RTC interrupt frequency and thereby the SAADC sampling frequency
#define SAADC_SAMPLE_INTERVAL_MS 250 //Interval in milliseconds at which RTC times out and triggers SAADC sample task (
#define SAADC_CALIBRATION_INTERVAL 5 //Determines how often the SAADC should be calibrated relative to NRF_DRV_SAADC_EVT_DONE event. E.g. value 5 will make the SAADC calibrate every fifth time the NRF_DRV_SAADC_EVT_DONE is received.
#define SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER 1 //Number of SAADC samples in RAM before returning a SAADC event. For low power SAADC set this constant to 1. Otherwise the EasyDMA will be enabled for an extended time which consumes high current.
#define SAADC_OVERSAMPLE NRF_SAADC_OVERSAMPLE_4X //Oversampling setting for the SAADC. Setting oversample to 4x This will make the SAADC output a single averaged value when the SAMPLE task is triggered 4 times. Enable BURST mode to make the SAADC sample 4 times when triggering SAMPLE task once.
#define SAADC_BURST_MODE 1 //Set to 1 to enable BURST mode, otherwise set to 0.
const nrf_drv_rtc_t rtc = NRF_DRV_RTC_INSTANCE(2); /**< Declaring an instance of nrf_drv_rtc for RTC2. */
static uint32_t rtc_ticks = RTC_US_TO_TICKS(SAADC_SAMPLE_INTERVAL_MS*1000, RTC_FREQUENCY);
static nrf_saadc_value_t m_buffer_pool[2][SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER];
static uint32_t m_adc_evt_counter = 0;
static bool m_saadc_calibrate = false;
static void rtc_handler(nrf_drv_rtc_int_type_t int_type)
{
uint32_t err_code;
if (int_type == NRF_DRV_RTC_INT_COMPARE0)
{
nrf_drv_saadc_sample(); //Trigger the SAADC SAMPLE task
LEDS_INVERT(BSP_LED_0_MASK); //Toggle LED1 to indicate SAADC sampling start
err_code = nrf_drv_rtc_cc_set(&rtc, 0, rtc_ticks, true); //Set RTC compare value. This needs to be done every time as the nrf_drv_rtc clears the compare register on every compare match
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
nrf_drv_rtc_counter_clear(&rtc); //Clear the RTC counter to start count from zero
}
}
static void lfclk_config(void)
{
ret_code_t err_code = nrf_drv_clock_init(); //Initialize the clock source specified in the nrf_drv_config.h file, i.e. the CLOCK_CONFIG_LF_SRC constant
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
nrf_drv_clock_lfclk_request(NULL);
}
static void rtc_config(void)
{
uint32_t err_code;
//Initialize RTC instance
nrf_drv_rtc_config_t rtc_config;
rtc_config.prescaler = RTC_FREQ_TO_PRESCALER(RTC_FREQUENCY);
err_code = nrf_drv_rtc_init(&rtc, &rtc_config, rtc_handler); //Initialize the RTC with callback function rtc_handler. The rtc_handler must be implemented in this applicaiton. Passing NULL here for RTC configuration means that configuration will be taken from the sdk_config.h file.
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
err_code = nrf_drv_rtc_cc_set(&rtc, 0, rtc_ticks, true); //Set RTC compare value to trigger interrupt. Configure the interrupt frequency by adjust RTC_CC_VALUE and RTC_FREQUENCY constant in top of main.c
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
//Power on RTC instance
nrf_drv_rtc_enable(&rtc); //Enable RTC
}
void saadc_callback(nrf_drv_saadc_evt_t const * p_event)
{
ret_code_t err_code;
if (p_event->type == NRF_DRV_SAADC_EVT_DONE) //Capture offset calibration complete event
{
LEDS_INVERT(BSP_LED_1_MASK); //Toggle LED2 to indicate SAADC buffer full
if((m_adc_evt_counter % SAADC_CALIBRATION_INTERVAL) == 0) //Evaluate if offset calibration should be performed. Configure the SAADC_CALIBRATION_INTERVAL constant to change the calibration frequency
{
m_saadc_calibrate = true; // Set flag to trigger calibration in main context when SAADC is stopped
}
NRF_LOG_INFO("ADC event number: %d\r\n",(int)m_adc_evt_counter); //Print the event number on UART
for (int i = 0; i < p_event->data.done.size; i++)
{
NRF_LOG_INFO("%d\r\n", p_event->data.done.p_buffer[i]); //Print the SAADC result on UART
}
if(m_saadc_calibrate == false)
{
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_buffer_convert(p_event->data.done.p_buffer, SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER); //Set buffer so the SAADC can write to it again.
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
}
m_adc_evt_counter++;
}
else if (p_event->type == NRF_DRV_SAADC_EVT_CALIBRATEDONE)
{
LEDS_INVERT(BSP_LED_2_MASK); //Toggle LED3 to indicate SAADC calibration complete
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_buffer_convert(m_buffer_pool[0], SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER); //Set buffer so the SAADC can write to it again.
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_buffer_convert(m_buffer_pool[1], SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER); //Need to setup both buffers, as they were both removed with the call to nrf_drv_saadc_abort before calibration.
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
NRF_LOG_INFO("SAADC calibration complete ! \r\n"); //Print on UART
}
}
void saadc_init(void)
{
ret_code_t err_code;
nrf_drv_saadc_config_t saadc_config;
nrf_saadc_channel_config_t channel_config;
//Configure SAADC
saadc_config.low_power_mode = true; //Enable low power mode.
saadc_config.resolution = NRF_SAADC_RESOLUTION_12BIT; //Set SAADC resolution to 12-bit. This will make the SAADC output values from 0 (when input voltage is 0V) to 2^12=4096 (when input voltage is 3.6V for channel gain setting of 1/6).
saadc_config.oversample = SAADC_OVERSAMPLE; //Set oversample to 4x. This will make the SAADC output a single averaged value when the SAMPLE task is triggered 4 times.
saadc_config.interrupt_priority = APP_IRQ_PRIORITY_LOW; //Set SAADC interrupt to low priority.
//Initialize SAADC
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_init(&saadc_config, saadc_callback); //Initialize the SAADC with configuration and callback function. The application must then implement the saadc_callback function, which will be called when SAADC interrupt is triggered
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
//Configure SAADC channel
channel_config.reference = NRF_SAADC_REFERENCE_INTERNAL; //Set internal reference of fixed 0.6 volts
channel_config.gain = NRF_SAADC_GAIN1_6; //Set input gain to 1/6. The maximum SAADC input voltage is then 0.6V/(1/6)=3.6V. The single ended input range is then 0V-3.6V
channel_config.acq_time = NRF_SAADC_ACQTIME_10US; //Set acquisition time. Set low acquisition time to enable maximum sampling frequency of 200kHz. Set high acquisition time to allow maximum source resistance up to 800 kohm, see the SAADC electrical specification in the PS.
channel_config.mode = NRF_SAADC_MODE_SINGLE_ENDED; //Set SAADC as single ended. This means it will only have the positive pin as input, and the negative pin is shorted to ground (0V) internally.
if(SAADC_BURST_MODE)
{
channel_config.burst = NRF_SAADC_BURST_ENABLED; //Configure burst mode for channel 0. Burst is useful together with oversampling. When triggering the SAMPLE task in burst mode, the SAADC will sample "Oversample" number of times as fast as it can and then output a single averaged value to the RAM buffer. If burst mode is not enabled, the SAMPLE task needs to be triggered "Oversample" number of times to output a single averaged value to the RAM buffer.
}
channel_config.pin_p = NRF_SAADC_INPUT_AIN0; //Select the input pin for the channel. AIN0 pin maps to physical pin P0.02.
channel_config.pin_n = NRF_SAADC_INPUT_DISABLED; //Since the SAADC is single ended, the negative pin is disabled. The negative pin is shorted to ground internally.
channel_config.resistor_p = NRF_SAADC_RESISTOR_DISABLED; //Disable pullup resistor on the input pin
channel_config.resistor_n = NRF_SAADC_RESISTOR_DISABLED; //Disable pulldown resistor on the input pin
//Initialize SAADC channel
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_channel_init(0, &channel_config); //Initialize SAADC channel 0 with the channel configuration
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_buffer_convert(m_buffer_pool[0],SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER); //Set SAADC buffer 1. The SAADC will start to write to this buffer
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
err_code = nrf_drv_saadc_buffer_convert(m_buffer_pool[1],SAADC_SAMPLES_IN_BUFFER); //Set SAADC buffer 2. The SAADC will write to this buffer when buffer 1 is full. This will give the applicaiton time to process data in buffer 1.
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
}
/**
* @brief Function for main application entry.
*/
int main(void)
{
LEDS_CONFIGURE(LEDS_MASK); //Configure all leds
LEDS_OFF(LEDS_MASK); //Turn off all leds
NRF_POWER->DCDCEN = 1; //Enabling the DCDC converter for lower current consumption
uint32_t err_code = NRF_LOG_INIT(NULL);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code); //Configure Logging. LOGGING is used to show the SAADC sampled result. Default is UART, but RTT can be configured in sdk_config.h
NRF_LOG_DEFAULT_BACKENDS_INIT();
NRF_LOG_INFO("SAADC Low Power Example.");
lfclk_config(); //Configure low frequency 32kHz clock
rtc_config(); //Configure RTC. The RTC will generate periodic interrupts. Requires 32kHz clock to operate.
saadc_init(); //Initialize and start SAADC
while (1)
{
if(m_saadc_calibrate == true)
{
nrf_drv_saadc_abort(); // Abort all ongoing conversions. Calibration cannot be run if SAADC is busy
NRF_LOG_INFO("SAADC calibration starting..."); //Print on UART
while(nrf_drv_saadc_calibrate_offset() != NRF_SUCCESS); //Trigger calibration task
m_saadc_calibrate = false;
}
while(NRF_LOG_PROCESS() != NRF_SUCCESS);
nrf_pwr_mgmt_run();
}
}
Thanks
Nick