This blog introduces how to create tunnel broker service in order to support IPv6 on your IPv4 network. The tunnel broker is providing IP conversion service with 6in4.
Preparation
- Raspberry Pi with Installed raspbian and 6LowPAN module
Following IoT SDK pages
Step by Step creating tunnel broker
-
Go to HE website
-
Create your account
※ Needs verification your account on your written email address after created account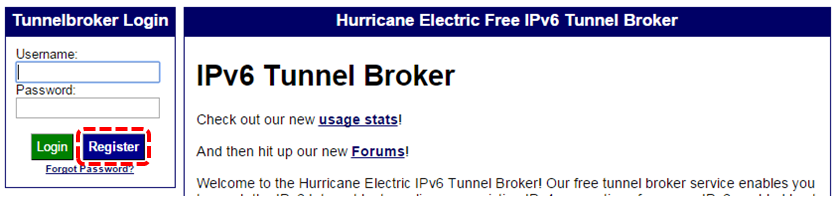
-
Login and Create Regular Tunnel
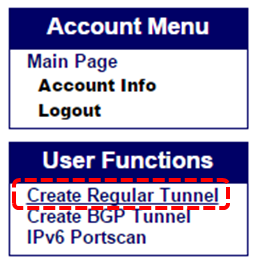
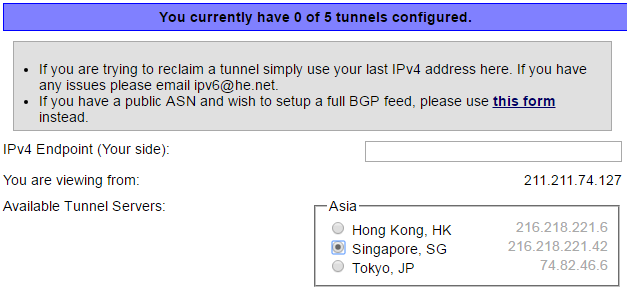
- Insert your own IPv4 address and select closest server by your location (In this case “Tokyo,JP”)
▣ IPv4 address should be same as shown on the web page
▣ It will check automatically after you entered your IPv4 address
※ if you have issue as below you need to configure router to allow pinging from external server
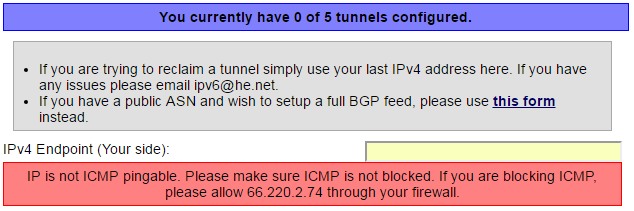
For My case I enabled WAN ping response feature on my router
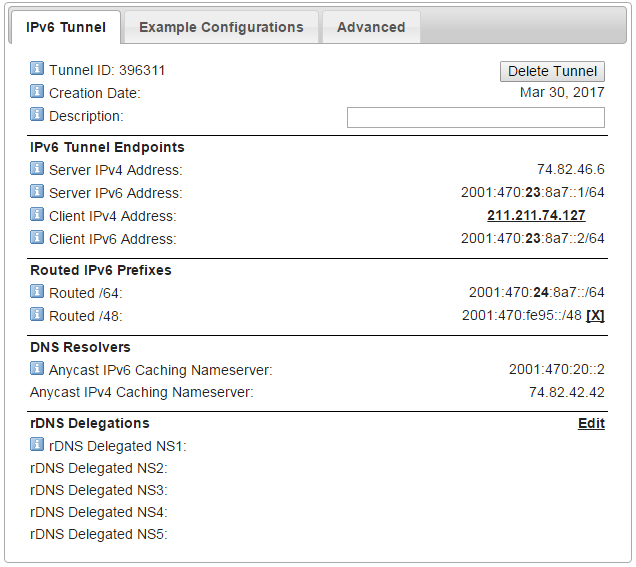
 5. You can get details of tunnel broker information after successfully create tunneling service
5. You can get details of tunnel broker information after successfully create tunneling service
- To easily set up tunneling service on your device it provides example configuration.
- Click "Example configurations" tab on "Tunnel Details" web page and select "Debian/Ubuntu" for linux OS
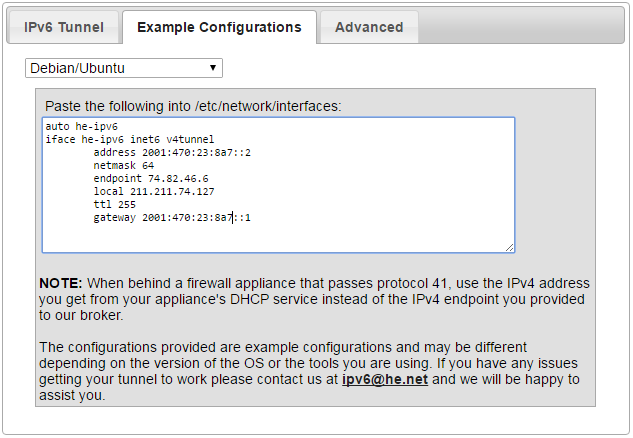
- Copy and add this information to RPi. interface file
- Click "Example configurations" tab on "Tunnel Details" web page and select "Debian/Ubuntu" for linux OS
$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
auto he-ipv6
iface he-ipv6 inet6 v4tunnel
address 2001:470:23:8a7::2
netmask 64
endpoint 74.82.46.6
local 211.211.74.127
ttl 255
gateway 2001:470:23:8a7::1
Tips. Setting for internal network (for NAT)
If you are in NAT network you can use your internal network IP address
$ sudo vi /etc/network/interfaces
auto he-ipv6
iface he-ipv6 inet6 v4tunnel
address 2001:470:23:8a7::2
netmask 64
endpoint 74.82.46.6
local 192.168.0.190
ttl 255
gateway 2001:470:23:8a7::1
- Assign IPv6 address to RPi. ethernet port. (in my case used 48bit prefix)
up ip addr add 2001:470:fe95:aaaa::1/64 dev eth0
down ip addr add 2001:470:fe95:aaaa::1/64 dev eth0
- Configure RADVD configration file.
$ sudo vi /etc/radvd.conf interface eth0
{
AdvSendAdvert on;
AdvHomeAgentFlag off;
MinRtrAdvInterval 30;
MaxRtrAdvInterval 100;
AdvDefaultLifetime 9000;
prefix 2001:470:fe95:aaaa::/64
{
AdvOnLink off;
AdvAutonomous on;
AdvRouterAddr on;
AdvValidLifetime infinity;
AdvPreferredLifetime infinity;
DeprecatePrefix on;
};
};
- reboot RPi.
$ sudo reboot- Now you have own your IPv6 address and network!!
Sample configuration files
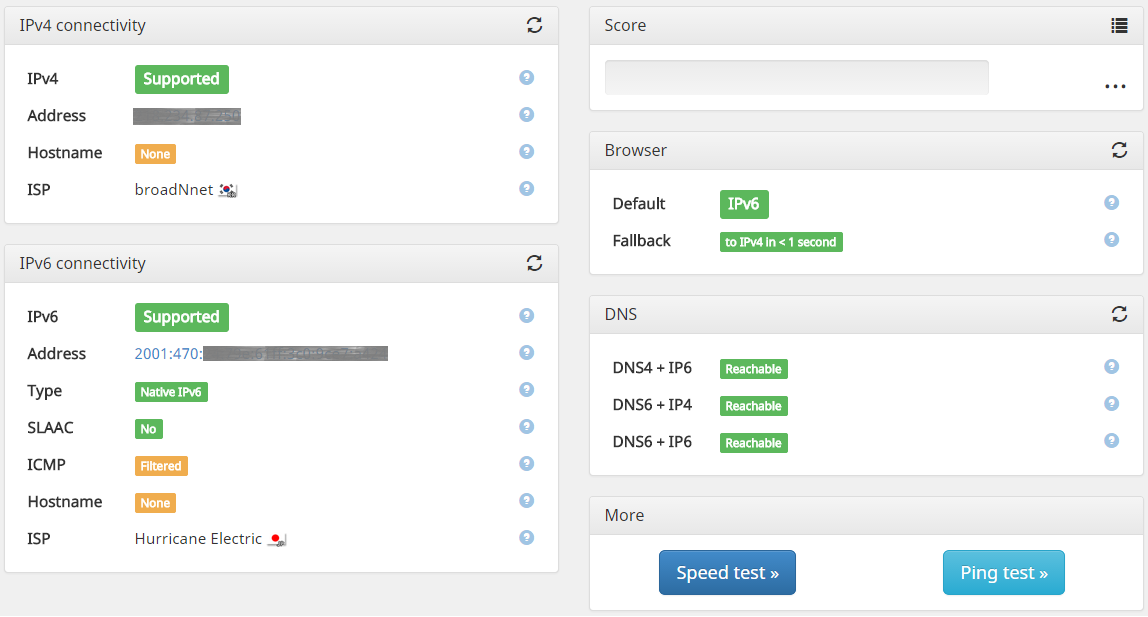
Tips!! IPv6 Verification
You can verify your IPv6 configuration whether it works correctly

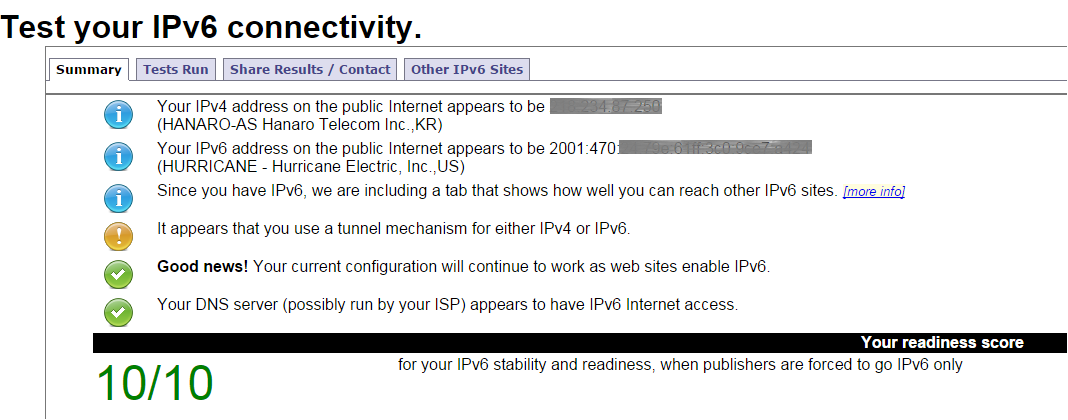

-

Eugene Yu
-
Cancel
-
Vote Up
0
Vote Down
-
-
Sign in to reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Comment-

Eugene Yu
-
Cancel
-
Vote Up
0
Vote Down
-
-
Sign in to reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Children