Hello,
I need to implement Find My Device for nRF52833.
From Sample I could find "samples/bluetooth/fast_pair/Locator Tag" example. I tried to go through it. but I could not able to map with fast pair specification(Fast Pair | Google for Developers).
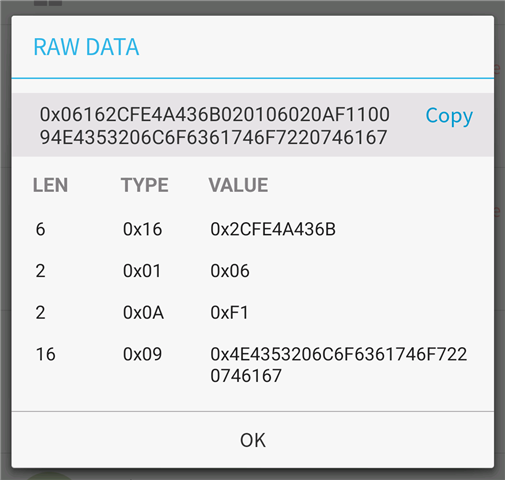
I want to check in which function advertisement is prepared ?
How keys(account keys,anti-snoofing keys) are sent in encrypted ?
In the advertisement which data we are sending(like fast pair UUID, Model id, anti snoofing keys, unique mac address,salt field ) etc ?