Good evening, (I have a few questions which are at the bottom, so I hope you don't mind me having posted the full length of these two programs first)
I've managed to produce some great results in developing PPM (pulse position modulation; related to PWM pulse width modulation) for a head tracker project I'm working on. I've included two fundamentally different programs as described below, which I'm testing using my Nano 33 BLE via the Arduino development environment...
Method 1: Servo PPM using 2 timers (4 channels)
This method produces the best results (although method 2 does indeed work quite well). The servos move virtually perfectly smooth almost 100% of the time. Timer 3 CC[0] sets the initial high value of the waveform, followed by CC[1] to [4] for the 4 channels. CC[5] is used for the PPM frame length which is set to 22500 microseconds. Each timer 3 compare activates timer 4 which in turn controls the pulse length.
The GPIOTE tasks are controlled by timer events via PPI channels. One complete frame length is processed by timer 3 independent of timer 3 IRQ handler. After the frame is complete, timer 3 stops and clears, then the new servo values are transferred, and the timer is started again. The delay until the next frame starts is dependent on timer 3 prescaler which is set to 1MHz, which could be increased, and the PPM channel values scaled accordingly.
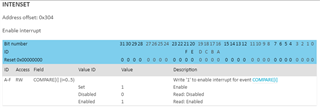
Note: I've omitted all Timer "_Pos" instructions except for TIMER_INTENSET (for GPIOTE I decided to just leave them all in place). _Pos is required for INTENSET even though it has only one field in its register (note "Write 1 to enable..." in the description. Without _Pos it doesn't work). Although SHORTS has 2 fields in its register, it doesn't need _Pos because I'm using its 1st field.
#include <nrf.h>
#define PPI_CHANNEL_0 (0)
#define PPI_CHANNEL_1 (1)
#define PPI_CHANNEL_2 (2)
#define PPI_CHANNEL_3 (3)
#define PPI_CHANNEL_4 (4)
#define PPI_CHANNEL_5 (5)
// #define PIN_GPIO (16) // Green for Nano 33 BLE
#define PIN_GPIO (2)
#define PORT (1)
/* Using timer 1 via MBED doesn't work, so perhaps it's being used */
void setup()
{
// Configure PIN_GPIO as output
// ----------------------------
NRF_GPIO->DIRSET = (1UL << PIN_GPIO);
// Configure GPIOTE
// ----------------
NRF_GPIOTE->CONFIG[0] =
(GPIOTE_CONFIG_MODE_Task << GPIOTE_CONFIG_MODE_Pos) |
(PORT << GPIOTE_CONFIG_PORT_Pos) |
(PIN_GPIO << GPIOTE_CONFIG_PSEL_Pos);
// Configure TIMER3 & TIMER4 to generate EVENTS_COMPARE[n]
// -------------------------------------------------------
NRF_TIMER3->BITMODE = TIMER_BITMODE_BITMODE_32Bit;
NRF_TIMER3->PRESCALER = 4;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[0] = 1000; // Values [0] to [4] set here can be anything because they're set in TIMER3_IRQHandler_v
NRF_TIMER3->CC[1] = 2500;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[2] = 4000;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[3] = 5500;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[4] = 7000;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[5] = 22500; // PPM Frame length
NRF_TIMER3->INTENSET = TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE5_Enabled << TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE5_Pos;
NVIC_EnableIRQ(TIMER3_IRQn);
NRF_TIMER3->TASKS_START = 1;
// Pulse length timer
// ------------------
NRF_TIMER4->MODE = TIMER_MODE_MODE_Timer;
NRF_TIMER4->BITMODE = TIMER_BITMODE_BITMODE_32Bit;
NRF_TIMER4->SHORTS = TIMER_SHORTS_COMPARE0_CLEAR_Enabled;
NRF_TIMER4->PRESCALER = 4; // 1MHz
NRF_TIMER4->CC[0] = 500; // Pulse length
// Configure PPI channels with connection between TIMER->EVENTS_COMPARE[n] and GPIOTE->TASKS_SET[0]
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_0].EEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[0];
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_0].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_SET[0];
NRF_PPI->FORK[PPI_CHANNEL_0].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->TASKS_START;
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_1].EEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[1];
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_1].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_SET[0];
NRF_PPI->FORK[PPI_CHANNEL_1].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->TASKS_START;
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_2].EEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[2];
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_2].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_SET[0];
NRF_PPI->FORK[PPI_CHANNEL_2].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->TASKS_START;
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_3].EEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[3];
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_3].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_SET[0];
NRF_PPI->FORK[PPI_CHANNEL_3].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->TASKS_START;
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_4].EEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[4];
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_4].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_SET[0];
NRF_PPI->FORK[PPI_CHANNEL_4].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->TASKS_START;
// --------------------------------------------------------------------
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_5].EEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->EVENTS_COMPARE[0]; // Control pulse length
NRF_PPI->CH[PPI_CHANNEL_5].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_GPIOTE->TASKS_CLR[0];
NRF_PPI->FORK[PPI_CHANNEL_5].TEP = (uint32_t) & NRF_TIMER4->TASKS_STOP;
// Enable PPI channels
// -------------------
NRF_PPI->CHENSET = (1UL << PPI_CHANNEL_0);
NRF_PPI->CHENSET = (1UL << PPI_CHANNEL_1);
NRF_PPI->CHENSET = (1UL << PPI_CHANNEL_2);
NRF_PPI->CHENSET = (1UL << PPI_CHANNEL_3);
NRF_PPI->CHENSET = (1UL << PPI_CHANNEL_4);
NRF_PPI->CHENSET = (1UL << PPI_CHANNEL_5);
}
volatile int initial_off_period = 1000; // The off period will always remain the same, therefore this initial value is arbitrary
volatile int chan1 = 1500;
volatile int chan2 = 1500;
volatile int chan3 = 1500;
volatile int chan4 = 1500;
void loop()
{
while (1)
{
// __WFE();
}
}
extern "C" void TIMER3_IRQHandler_v (void)
{
// volatile uint32_t dummy;
static int travel_rate = 5;
if (NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[5] == 1)
{
NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[5] = 0;
NRF_TIMER3->TASKS_STOP = 1;
NRF_TIMER3->TASKS_CLEAR = 1;
// Read back event register to ensure we have cleared it before exiting IRQ handler
// dummy = NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[5];
// dummy; // To get rid of set but not used warning
chan1 += travel_rate;
chan2 += travel_rate;
chan3 += travel_rate;
chan4 += travel_rate;
if (chan1 > 1900)
{
chan1 = 950;
chan2 = 950;
chan3 = 950;
chan4 = 950;
}
NRF_TIMER3->CC[0] = initial_off_period;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[1] = NRF_TIMER3->CC[0] + chan1;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[2] = NRF_TIMER3->CC[1] + chan2;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[3] = NRF_TIMER3->CC[2] + chan3;
NRF_TIMER3->CC[4] = NRF_TIMER3->CC[3] + chan4;
NRF_TIMER3->TASKS_START = 1;
}
}
Method 2: Servo PPM using 1 timer (8 channels)
Unlike method 1, the entire PPM waveform is constructed inside the timer handler and therefore is dependent on its timing accuracy/consistency. You can have as many channels as PPM supports, even though only one timer is being used. I've added a demo option which requires setting the "demo_multiplier" value and "sigPin" to an LED.
Synchronisation seems like a key point. For example, by considering method 1, it's clear that all 4 channel values are transferred whilst the timer is stopped. However for this single timer method, the channel values are transferred without stopping the timer. **Refer to the 5th post for clarification about this**
// The following program is adapted from here: https://forum.arduino.cc/t/mbed-os-isr-linkage-on-arduino-33-ble/898811 and here: https://quadmeup.com/generate-ppm-signal-with-arduino
// -------------------------------------------
#include <nrf_timer.h>
NRF_TIMER_Type* timer = NRF_TIMER4;
IRQn_Type timer_irq = TIMER4_IRQn;
#define NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS 8 // Number of channels
#define CHANNEL_DEFAULT_VALUE 950 // Default servo value
#define FRAME_LENGTH 22500 // PPM frame length in microseconds (1ms = 1000µs)
#define PULSE_LENGTH 500 // Pulse length
#define sigPin 10 // 23 is the Nano 33 BLE Green LED. 10 is ~D10... See here for pin definitions: https://github.com/arduino/ArduinoCore-nRF528x-mbedos/blob/master/variants/ARDUINO_NANO33BLE/pins_arduino.h#L54
volatile int demo_multiplier = 1; // 200 is good for testing via the onboard LEDs (Don't forget to change "sigPin" above)
volatile int ppm [NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS];
extern "C" void TIMER4_IRQHandler_v()
{
static int cur_chan_numb;
static unsigned int calc_rest;
static bool state = true;
if (timer->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] == 1)
{
timer->EVENTS_COMPARE[0] = 0;
if (state) // Start pulse
{
digitalWrite (sigPin, HIGH); // On state
timer->CC[0] = PULSE_LENGTH * demo_multiplier;
state = false;
}
else // End pulse and calculate when to start the next pulse
{
state = true;
digitalWrite (sigPin, LOW); // Off state
if (cur_chan_numb >= NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS)
{
cur_chan_numb = 0;
calc_rest = calc_rest + PULSE_LENGTH;
timer->CC[0] = (FRAME_LENGTH - calc_rest) * demo_multiplier;
calc_rest = 0;
}
else
{
timer->CC[0] = (ppm[cur_chan_numb] - PULSE_LENGTH) * demo_multiplier;
calc_rest = calc_rest + ppm[cur_chan_numb];
cur_chan_numb++;
}
}
}
}
void setupTimer (NRF_TIMER_Type* timer, unsigned int timer_period)
{
timer->MODE = NRF_TIMER_MODE_TIMER;
timer->BITMODE = TIMER_BITMODE_BITMODE_32Bit;
timer->SHORTS = TIMER_SHORTS_COMPARE0_CLEAR_Enabled;
timer->PRESCALER = NRF_TIMER_FREQ_1MHz;
timer->CC[0] = timer_period;
timer->INTENSET = TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE0_Enabled << TIMER_INTENSET_COMPARE0_Pos;
NVIC_EnableIRQ (timer_irq);
timer->TASKS_START = 1;
}
void setup()
{
pinMode (sigPin, OUTPUT);
setupTimer (timer, 10000); // Setup timer registers and start timer. Note that this value here is quite arbitrary because it's set in TIMER4_IRQHandler_v()
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS; ++i)
// ppm[i] = CHANNEL_DEFAULT_VALUE;
ppm[i] = 950 + i * 100; // This produces a varied but consistent offset LED demo via demo_multiplier
}
float currentTime = 0;
float previousTime = 0;
float deltaTime = 0;
void loop()
{
if (demo_multiplier == 1) // Don't run here for LED demo
{
currentTime = micros();
deltaTime += currentTime - previousTime;
previousTime = currentTime;
if (deltaTime > 10000) // 100Hz
{
deltaTime = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS; ++i)
if (ppm[i] > 1900)
ppm[i] = 950;
else
ppm[i] += 3;
}
}
}
Here are my questions
- When are timer CC values updated if the transfer is initiated whilst the timer is running?
- Commented in timer 3 handler for method 1 is "dummy" from here Nordic Timer Example. I thought that "NRF_TIMER3->EVENTS_COMPARE[n] = 0" took care of that, so please kindly explain to me what the two dummy lines do?
- How important is __WFE() and what does it do? (I have it commented, and everything seems fine)
- With respect to the findings as detailed in my "Note:" near the beginning of this post in relation to INTENSET for Timer, please explain why _Pos is required even though INTENSET's register only has one field?
- Please advise of any improvements for either method? Although both work well, method 1 as I already said is very smooth but limited to 4 channels via two timers, unless for example reusing the CC values by using a timer handler via EVENTS_COMPARE[4] to stop it, transfer the next set of PPM values, and restart again. Like it's already doing but two stages instead of one, but that would of course introduce a timer handler interruption part way in constructing the waveform.