Hello,
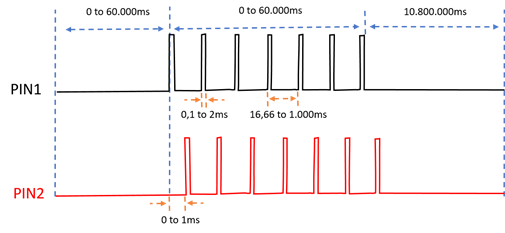
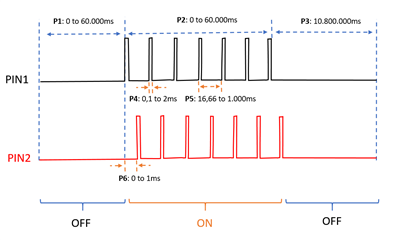
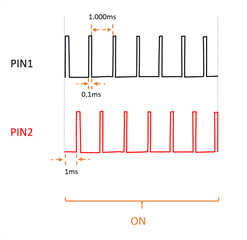
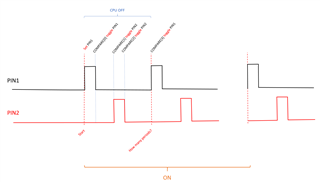
Considering the waveforms in the following chart, which will be the best approach to keep the power consumption as low as possible?
Specifically, which peripheral is suggested (i.e. pwm, timer, ppi)?
The two (2) waveform are identical, except for the delay between (0 to 2ms).
Thanks